UNDERSTANDING SKIN IS OUR MISSION!
A baby’s skin shows a significant loss in trans-epidermalwater (TEWL), a high pH, desquamations, rapid cellregeneration, a high water content despite the highlevel of NMF (natural moisturizing factor) and a lipid concentration on the surface which is lower than that found in the skin of adults.
CHILDREN SKIN'S STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
The outer layer of the epidermis, said stratum corneum, is much thinner and cells are less closely related in babies and kids’ skin than in the skin of an adult. Even the sweat and sebaceous glands are less active, and so the hydrolipidic film (emulsion of water and fat that covers and protects the skin's surface) and the protective acid mantle (the part of water of the hydro-lipid film, which is slightly acidic) are still relatively weak.
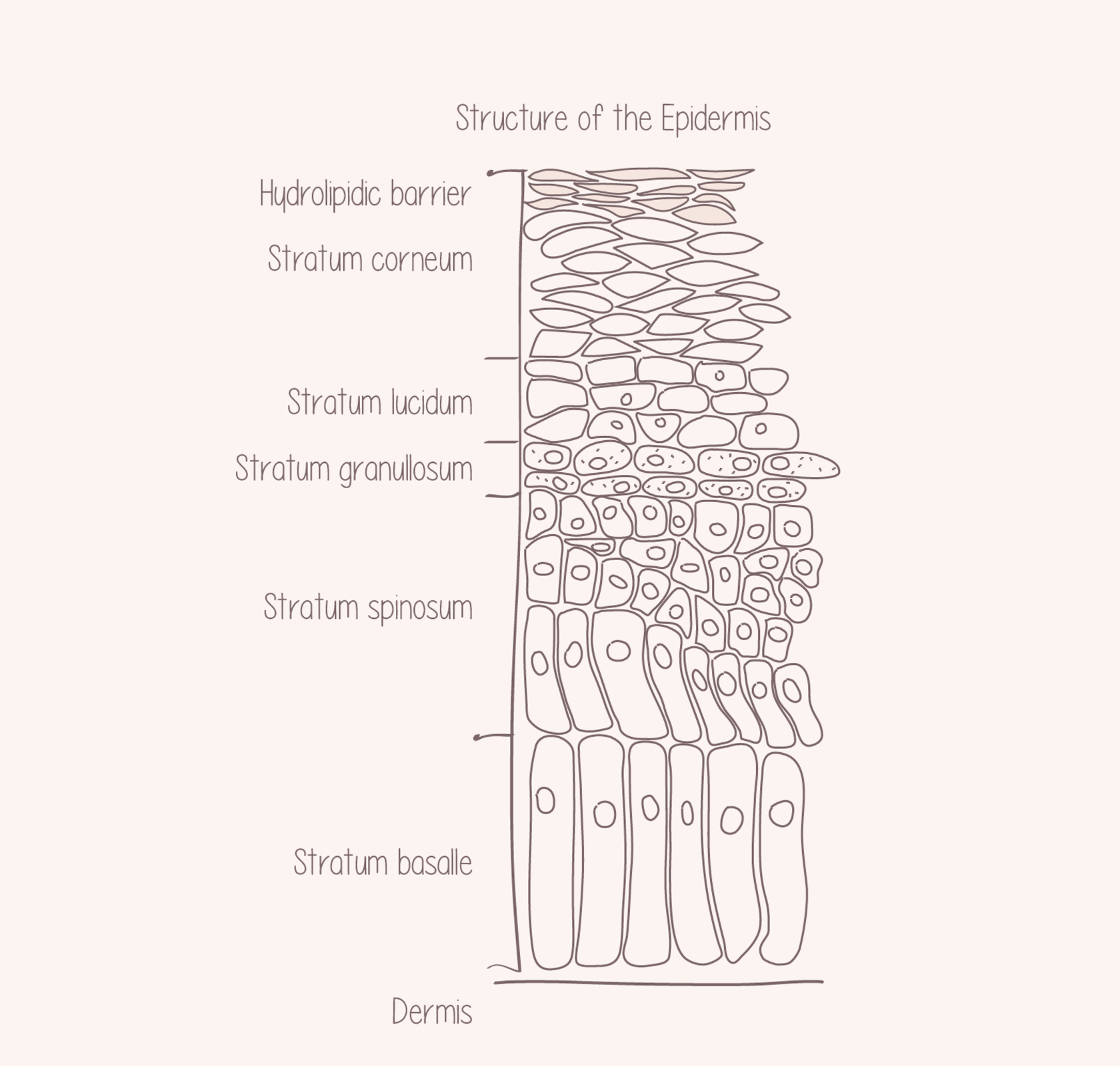
As a consequence, the barrier function is more limited:
- Children's skin is less resistant than adults’ and is especially sensitive to chemical, physical and microbial aggression: The substances that come into contact with children's skin are more easily absorbed and penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin.
- Children's skin tends to dehydrate.
- Children’s skin is more sensitive to UV rays than adults.



HOW TO TAKE CARE OF THE SKIN OF CHILDREN?
Children's skin needs special attention:
- Use mild detergents: alkaline soaps are aggressive on the skin, remove lipids and dehydrate.
- Limit your bath time: Hot water and long baths remove the lipids of the skin. Reduce the time and use warm water rather than hot.
- Take care: Regular moisturizing with pediatrician tested products on sensitive skin, and with proven skin compatibility, helps keeping it hydrated and healthy.
- Always protect children's skin from harmful UV rays.